Topological Analysis and Network Operations
Implementation
Since the new changes have been introduced into the topological analysis
(2003.11), the construction of both homogeneous and heterogeneous networks can
be performed by the selection of single node in the "NetNode definition" dialog
shown below or on the Generation step in the 'Generation Options'
dialog. The construction of such topological networks works only if one
uniatomic node exists in the the net. In case of more complex networks use the
"specific atom" section of the "Net Node Definition" dialog. The definition of
the single uniatomic node allows the automatic identification of the other
multiatomic nodes. Sometimes the software needs to consider some auxiliary atoms
as nodes, but after all it does not include them in resulting vertex symbol.
An example of that is a network with multidentate ligands and two types of
homogeneous metal centres - multicoordinate and bicoordinate. To identify
ligands the software needs to know about both metal centres as they
identify the ligands (something between two or more metal centres is the
ligand). However, the bidentate "nodes" will be excluded from the resulting
symbol, giving correct ring sizes. Further limitations of the software are
described in the introduction.Construction of homogeneous and heterogeneous topological networks with
single
uniatomic node can be done by the selection of the
network node in 'Generation Options'
dialog box. Simply select the chemical element, which will play the role of topological node and
generate the extended structure. After end of the generation process, the
network bonds becomes accessible via the corresponding command of
main toolbar. The construction of the
topological networks can be done after structure generation and is discussed
below.
More complicated heterogeneous topological networks (consisting of nodes of different types) can be constructed using 'Topological
Analysis' command of the main menu. The command launches 'Net Node definition'
dialog box, which allows the definition of multiple network nodes. The networks
with only one type of uniatomic node can be transformed into their topological
equivalents by the selection of the node type of that uniatomic node.
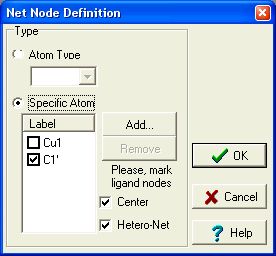 |
Homogeneous and heterogeneous networks with only one uniatomic node networks can be constructed using this dialog by
selecting the 'Atom Type' option or by adding one specific atom to the list.
Multiple nodes can be different metal centres, different ligands etc. The
ligand node can be defined by any of it's atoms directly not connected to
any other node, and the ligands should be
separated by uniatomic nodes to make the analysis correct. Use 'Add' button,
which shows 'Add Net Node' dialog, to add new node to the list. The selected
atoms should be separated at least by one non-nodal atom. A
'dummy' atom can be placed in the centre of a ligand and used in topological analysis to create a more symmetrical
network. This can be achieved by checking corresponding checkbox and ligand
atoms.
'Hetero-Net' - if the checkbox is checked, then bonds between the
same nodes are automatically removed.
Some notes about constructing complex topological networks see at
Bonds List. |
| View of the 'Net Node Definition' dialog |
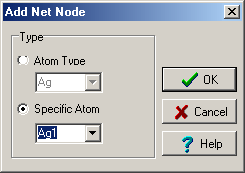 |
This is an auxiliary dialog for 'Net Node Definition'
dialog. The dialog allows selection of networks nodes. If 'atom type'
selected and structure contains more then one element of such type in the
asymmetric unit, then all of those atoms will be placed to the list of
nodes. Otherwise only specific atom (identified by its label) will be
inserted. |
| View of the 'Add Net Node' dialog |
Notes:
An "edge effect" appears when the asymmetric unit contains parts of ligands. It
appears like strange topological bonds existing at the edges of net.. However
these bonds can be removed from the network using 'Extract from net' command of
the
Bonds List window.
©
Oleg V. Dolomanov, 2003
Last Updated 2003.12.04

